In this tutorial series, I'll guide through MongoDB's Aggregation framework and let you harness its powers to become a more efficient MongoDB user.
I won't assume any prior experience in this article. It's for you if you'd like to take your MongoDB skills to the next level and leverage its aggregation framework to perform even more expressive queries.
This blog series will dive deep into the aggregation framework as well as introduce you to some of the newly added features to MongoDB.
What is the Aggregation Framework?
Aggregations operations process data records and return computed results. Aggregation operations group values from multiple documents together and can perform a variety of operations on the grouped data to return a single result. In SQL count(*) and with the group by is an equivalent of MongoDB aggregation.
Why use the aggregation framework?
Expressive Filters
It gives a powerful set of tools to perform a wide variety of operations such as filtering, sorting, and grouping data.
Data Transformations
It allows you to transform your data in a very efficient manner. You could utilize aggregation operators to perform calculations and more.
Statistical Utilities and Data Analysis
You can use MongoDB Aggregation to perform powerful data analysis.
My previous job relied on the MongoDB aggregation framework to deliver statistical data for visualisations and decision making and that's why I grew to appreciate this framework.
There's plenty more that you can do with this powerful tool!
How to perform Aggregation in MongoDB?
Map-Reduce
The official MongoDB documentation site recommends using the Aggregation Pipeline for most use cases due to its simplicity and expressive nature.
An aggregation pipeline provides better performance and usability than a map-reduce operation.
Single Purpose Aggregation Functions
MongoDB also provides db.collection.estimatedDocumentCount(), db.collection.count() and db.collection.distinct().
All of these operations aggregate documents from a single collection. While these operations provide simple access to common aggregation processes, they lack the flexibility and capabilities of an aggregation pipeline.
Aggregation Pipelines
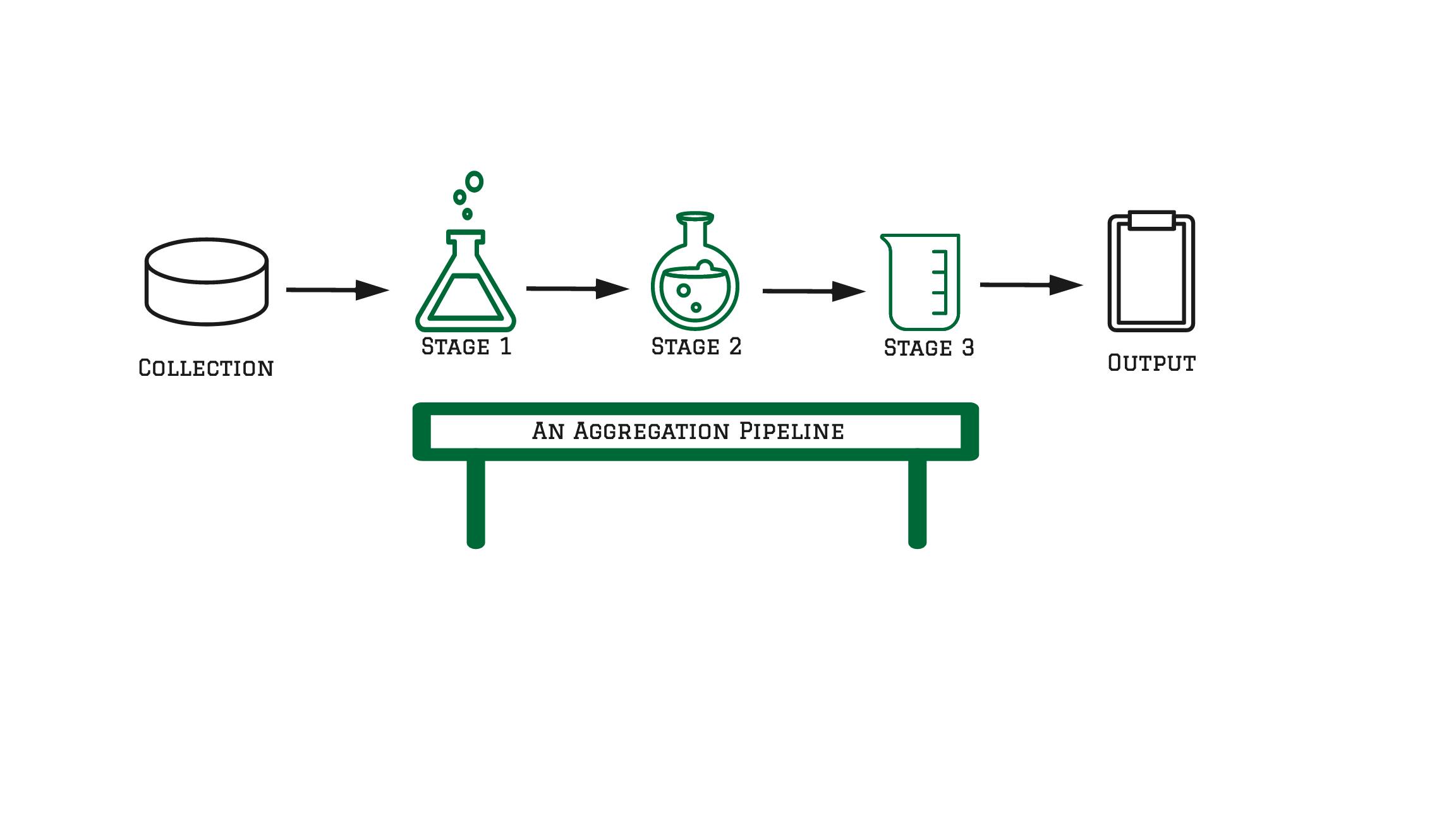 A visual representation of a MongoDB Aggregation Pipeline
A visual representation of a MongoDB Aggregation Pipeline
db.products.aggregate([{ $match: { discounted: true } }]);
A MongoDB query to perform an aggregation operation.
What are pipelines?
A pipeline is a data processing method that relies on steps. You must at least have one operation in your database to perform an aggregation query.
Aggregation Pipelines
The aggregation pipeline is a framework for data aggregation modeled on the concept of data processing pipelines. Documents enter a multi-stage pipeline that transforms the documents into aggregated results.
In simple terms, a pipeline is a composition of stages where data from each stage will serve as input to the next stage.
An aggregation pipeline consists of stages.
Stages
A stage is a data processing step. A stage could be used to derive insights from data, make changes, perform comparisons, and more. Logically, I like to categorize aggregation stages into the following
- CRUD Stages
- Data Analysis Stages
- Transformation stages
- Composition Stages
The structure and syntax
You can perform an aggregation via the aggregate() method which is available on your native driver.
This example will use TypeScript so make sure you have it installed!
We aggregate data using the MongoDB aggregate() method which is also available in mongoose.
It accepts an array that represents an aggregation pipeline.
This array could accept several objects with each being an aggregation stage.

